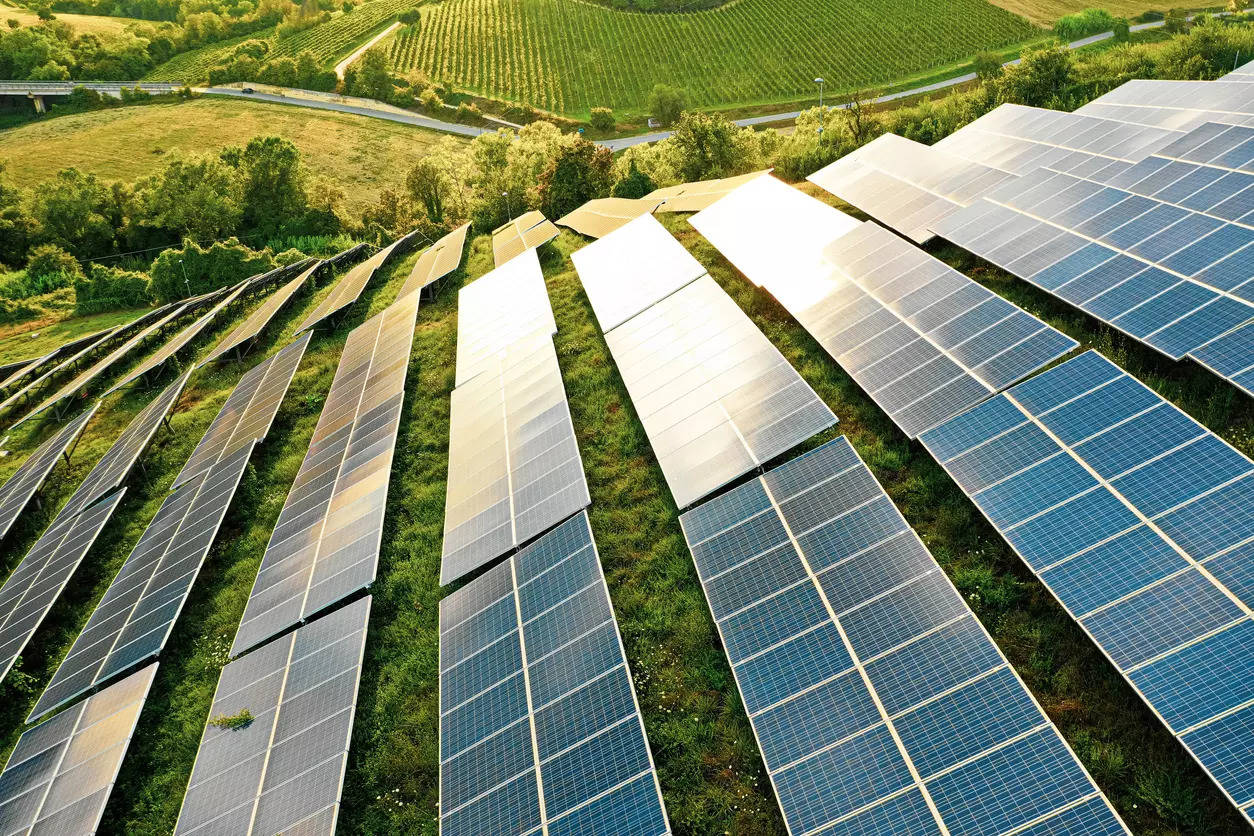
The production of an abundant and sustainable energy supply for future generations is feasible only with renewable energy. Before the awareness that renewable energy had the potential to improve our level of energy independence, it was a resource that mainly went unused for a long time. India has stepped up its efforts to reduce the nation’s overall carbon footprint and fulfil its Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) commitments, which it made as part of the Paris Agreement, in its quest to reach the $5 trillion economy goal by 2024–25 and rise to the third-largest economy by 2030. The government has set an ambitious target to install 500 GW of renewable energy by 2030, including 140 GW of wind and 280 GW of solar power. This goal will usher in a “green revolution” in the nation.Energy independence and indigenizing renewable manufacturing in India have become key priorities in pursuing sustainable development. India is one of the world’s economies, expanding quickly, with a population of more than 1.4 billion. Due to its fast industrialization and urbanization, India increasingly depends on imported fossil fuels to satisfy its rising energy needs. This dependence not only exposes the nation to shifts in the price of oil on a global scale but also causes considerable carbon emissions that fuel climate change. To attain energy independence and advance sustainable development, India must concentrate on growing its renewable energy sector and indigenizing its renewable manufacturing sector.Additionally, localizing renewable manufacturing in India will increase economic growth and job possibilities while reducing the nation’s reliance on imported renewable energy technology. India is significantly dependent on imports to satisfy its current demands for renewable equipment, notably solar photovoltaic (PV) cells and modules. However, India has the potential to become a global leader in solar manufacturing, given its abundant solar resources and skilled workforce. The government must establish regulations that support domestic manufacturing in the renewable energy sector and offer financial incentives to startups and local manufacturers.The Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) plan, which offers financial incentives to regional producers of renewable technology, is one such policy initiative the government has adopted. The government intends to fund indigenous producers of high-efficiency solar PV modules with Rs 25,000 crore (about USD 3 billion) over five years under this programme. This plan aims to decrease India’s reliance on imported machinery and boost indigenous industrial capabilities. However, these advantages are typically only available to large companies with deep pockets. The government should further stimulate indigenous manufacturing by providing ad hoc incentives for MSMEs and startups to encourage inclusive growth in the sector.
Imposing safeguard taxes on imported solar PV cells and modules is another government strategy that has worked. To defend against low-cost imports, the government has placed safeguard taxes on imported solar PV cells and module. These duties have helped in promoting domestic manufacturing, and several Indian companies have set up solar cell and module manufacturing facilities in the country.
Both public and private sectors will require more significant capital inputs to maintain increased development to raise their renewable energy capacity to 500 GW. Government organizations like IREDA play a crucial role in this. Additionally, the government should promote FDI by offering tax breaks and other incentives.
Additionally, a robust renewable equipment supply chain must be developed in India to manufacture products locally for the renewable industry. This entails the establishment of manufacturers, suppliers of raw materials, and infrastructure for logistics and transportation. The government must collaborate with regional producers to create a thorough supply chain to meet the nation’s rising need for renewable technology.
India’s sustainable growth depends on establishing energy independence and localizing renewable manufacturing. Therefore, the government must establish regulations supporting the domestic production of renewable equipment, offer financial incentives to regional producers, and create a robust supply chain. By doing this, India may lessen its reliance on imported machinery, increase employment possibilities, foster economic growth, and support efforts to tackle climate change worldwide.
India remains committed to achieving a sustainable future through renewable energy sources while ensuring economic growth. The country’s contribution towards building a greener world warrants commendation. The government is focusing heavily on transitioning to clean energy sources and is taking steps toward reducing its environmental footprint while increasing awareness about global warming.
[This piece was written by Abhay Adya, Business Head (Renewables), Zetwerk Manufacturing]